Male Infertility The Insight
About 15% of couples trying to get pregnant the first time fail. Most doctors make a diagnosis of primary infertility in cases where pregnancy does not occur within one year of regular sexual life without contraception.

According to statistics from 80-85% of couples conceiving occurs within 12 months of sexual activity without contraception, and situations where the pregnancy during this period of time not come, considered as a possible infertility, and patients should test. Data from the past 20 years show that approximately 30% of cases of problems with conception plays a role only male factor, and approximately 20% of the violations found both the husband and his wife.

Thus, male factor, at least in part, plays a role in 50% cases of infertility.
Major problems with identifying male factor infertility related to timing of the test, the most effective scheme of examination of men and the most rational forms of therapy and operative treatment methods. In solving the problem of infertility is extremely important to consider the couple as a unit to allow the simultaneous screening and treatment of both spouses. The longer the period of infertility, the lower the chances of a married couple to achieve a positive result. Many families are beginning to experience after several months of non-occurrence of pregnancy. In such cases, should not be encouraged to continue to expect a pregnancy without her husband's study. The initial stages of the survey men should be held whenever the patients treated with the main complaint of infertility. Such a survey should be quick, noninvasive and inexpensive.
Reproductive physiology of men. The axis of the hypothalamus
The hypothalamus - the main integrative center functional reproductive system in men. Receiving information from the central nervous system and testes, hypothalamus regulates the formation and secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). Neurotransmitters and neuropetides have both inhibitory and stimulating effect on the hypothalamus. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), secreted by the hypothalamus in a pulsating mode, which is a necessary step stimulation of synthesis and secretion of both gonadotropins pituitary (LH and FSH). It is interesting and ironic that the appointment of GnRH is not in the momentum, and in continuous operation results after the initial stimulation of pituitary gonadotropin release of the oppression of the allocation of LH and FSH. And luteinizing (LH) and follicle-stimulating (FSH), a hormone produced in the anterior lobe of the pituitary and secreted in a pulse mode in response to a pulsating production of GnRH. In the testes, LH and FSH bind to specific receptors on the Leydig cells and Sertoli. Testosterone, the main product of the internal secretion of the testis, is the main inhibitor of secretion of luteinizing hormone in men. In the peripheral tissues of testosterone can be converted into more potent androgen dihydrotestosterone, or a powerful estrogen - estradiol. Androgens and estrogens are formed independently regulate the secretion of LH.
Production of FSH is regulated by the mechanism of feedback of inhibion, formed in the Sertoli cells. The deterioration of spermatogenesis is accompanied by a decrease in formation and as a consequence (according to the mechanism of negative feedback) increased secretion of FSH. Isolated increase in FSH levels - an important marker of the state of germ cell epithelium of the testes.
Secretion of prolactin also has a complicated relationship with gonadotropic hormone. In men with hyperprolactinemia increased level of prolactin has an inhibitory effect on the secretion of GnRH. In addition to the suppression of secretion of LH and testosterone production increase in prolactin levels may have a direct impact on the central nervous system. In men with hyperprolactinemia receiving substitution therapy with testosterone, libido and sexual function were not restored until then, until a decrease in the level of prolactin.
Testicles. Leydig cells.
Testosterone is secreted in a pulsating mode of Leydig cells in response to the pulsating secretion of LH. For testosterone circadian rhythm of secretion, with peak secretion in the early morning and decreasing in the afternoon or evening.
In the intact egg after the exogenous administration of a number of LH receptors to LH in the testes is reduced as a result of Down-regulation. High doses of GnRH and its analogs may lead to a decrease in the number of LH receptors and thus suppress the secretion of LH. In practice, this feature is used to pharmacological castration in men with prostate cancer. Estrogens inhibit the activity of several enzymes involved in the synthesis of testosterone, and thus directly affect the formation of testosterone. There is also a inside ultra short feedback loop through which exogenous testosterone will override the effect of LH and inhibit production of endogenous testosterone. In healthy men, only 2% of circulating testosterone in the blood is in free or unbound state, 44% of testosterone associated with testosterone-estradiol-binding globulin (sex steroids globulin, SHBG), and 54% albumin or other proteins. These steroid proteins modulate the action of androgens. SHBG has a higher affinity for testosterone than for estradiol, and changes in SHBG levels leads to changes in hormonal levels. The level of SHBG is increased under the influence of estrogen in the treatment of thyroid hormones, liver cirrhosis, and may decline under the influence of androgens, growth hormone and obesity. The biological action of androgens appears to target-organs that contain specific protein receptors to androgen. Testosterone from the circulating blood enters the target cell, where under the influence of the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase into a more powerful androgen-dihydrotestosterone. The main effects of androgens in target-tissues include:
- Regulation of gonadotropin secretion of the hypothalamic-pituitary system;
- Initiation and maintenance of spermatogenesis;
- Differentiation of internal and external genitalia during fetal development;
- Promotion of sexual development at puberty.
Seminiferous tubules

Seminiferous tubules contain germ cells of the epithelium at different stages of maturation and their supporting Sertoli cells. Seminiferous tubules are up 85-90% of the testes. Sertoli cells represent a permanent population of nondividing cells microenvironment. They are located on the basement membrane of seminiferous tubules and are connected by dense formations (tight junctions). These dense connections with closely interconnected muscle cells peritubular space form hemato-testicular barrier. Functional significance of the hemato-testicular barrier is to create a unique microenvironment necessary for spermatogenesis, and maintenance of immune privilege of testis. This insulation is very important, because education is sperm puberty, which is much later serve as the immune system. If the formation of sperm was not immunologically protected, then the differential cells would be recognized, the immune system as foreign and destroyed would. Sertoli cells are involved, how to feed the developing sperm cells, and in the phagocytosis of dead cells. Spermatogonia and young spermatocytes located in the seminiferous tubules near the basal membrane and the maturing move in a more upper layers deep into the lumen of the tubules.
Germinal or spermatogenic, the cells are located in the seminiferous strictly defined way. Spermatogonia lie directly on the basement membrane and in the direction of the lumen of the tubules are arranged in series-WIDE primary spermatocytes, secondary spermatocytes and spermatids. Revealed 13 different types of germ cells of the epithelium, representing different stages of maturation of sperm.
Spermatogenesis

Spermatogenesis

A complex process in which the primitive germ cells or spermatogonia, divide, reproducing like a stem cell, or give rise to daughter cells subsequently differentiate into spermatocytes. Further division of spermatocytes gives rise to lines of cells that eventually differentiate into spermatids and further into sperm. Differentiation involves the condensation of the nucleus, acrosome formation, and loss of much of the cytoplasm, the formation of the tail and movement of mitochondria in the middle part of the sperm, which becomes the "engine room" cells, providing job tail. With germ cells of the epithelium, while getting into the processes of spermatogenesis, called a generation. The cells of one generation are on the same stage of development.
Six developmental stages of germ cell epithelium.

The development of sperm from the first stage to the sixth of a cycle. In humans, the duration of each cycle of approximately 16 days, but the way the transformation from early spermatogonia to mature sperm takes 4.6 cycles. Thus, the duration of spermatogenesis in humans is about 74 days.
Hormonal regulation of spermatogenesis
Between the two separate parts of the testis - seminiferous, and Environ-mental to the interstitial tissue - there is a close structural and functional relationship. Luteinizing hormone pituitary affect spermatogenesis indirectly by stimulating the production of testosterone. Target cells of FSH - Sertoli cells. Thus, FSH and testosterone - hormones that directly affect the epithelium of the seminiferous tubules. Androgen type protein formed Sertoli cells and involved in intracellular transport of testosterone, may play a role of testosterone in the reservoir tubules in addition to testosterone coming from the testicular tubules in the epididymis. A close relative position of Leydig cells and seminiferous tubules, as well as the formation of Sertoli cells of androgen-binding globulin, maintains a high concentration of testosterone in the microenvironment of differentiating cells of spermatogenesis. Hormonal changes needed to run spermatogenesis occur regardless of the process of maintaining spermatogenesis. In order to maintain spermatogenesis, for example, by turning off the pituitary gland, is necessary only testosterone. However, if the function of germ cell epithelium off in a lack of testosterone, then run spermatogenesis requires both FSH and testosterone.
Transport - maturation - Storage of sperm
Although, the formation of spermatozoa takes place in the egg, the processes of maturation, storage and transport of sperm provided by the epididymis (epididymis). Spermatozoa that are in seminiferous testis are immobile and incapable of fertilization. Their maturation is completed outside the egg in the ducts of the epididymis. Tortuous seminiferous tubules testicular end network testis, which in turn forms the efferent ducts (ductuli efferentes). These efferent tubules of testicular fluid and sperm come from eggs in the epididymis head. Parorchis or epididymis has a head, body and tail and consists of a single, highly twisted duct whose length is about 5-6 meters. Although the duration of transport in the stream epididymis varies depending on age and sexual activity of men, on average, this time is 4 days. In that period of maturation in the head and body of the epididymis sperm are becoming increasing mobility and the ability to fertilize an egg.

In addition to the maturation of sperm, testicular appendage acts as a "storage" or reservoir of male germ cells. It is estimated that the reservoir semen contains about 440 million sperm, more than 50% of which lies in the caudal part of epididymis. From the tail of the epididymis sperm enter the spermatic cord (vas deferens), which is a muscular tube length 30-35cm. The contents of spermatic cord through the peristaltic reductions wall duct enters semi basal channel (ductus ejaculatorius) and then through the emission and ejaculation in the urethra. During the emission of the secret of the seminal vesicles and prostate gland goes into the posterior urethra. Ejaculatory duct reduction and muscles of the bladder neck under the control of the sympathetic nervous system.
During ejaculation, the bladder neck muscles contracting and relaxing external sphincter, and the sperm moves from the urethra by rhythmic reductions perineal and bulbourethral muscles. It is established that the first portion of the ejaculate contains a small amount of fluid from the spermatic cord, but contains a large number of spermatozoa. The bulk of seminal fluid produced in the seminal vesicle and to a lesser extent - in the prostate. The seminal vesicles provide a nutritious substrate sperm - fructose, as well as prostaglandins and coagulating substance. An established function of seminal plasma is to create a buffer in the acidic environment vagina. Clot formed sperm after ejaculation, liquefies within 20-30 minutes under the influence of proteolytic enzymes of the prostate. Secret of the prostate also adds to the seminal fluid zinc ions, phospholipids, spermine, phosphatase. The first portion of ejaculate is characterized by a maximum content of sperm and secretion of the prostate, while the second portion is represented, first of all, the secret of the seminal vesicles and contains fewer sperm.
Fertilization
Typically, fertilization occurs in the fallopian tubes during ovulation. In per ovulatory period (in the middle of the menstrual cycle) is changing the cervical mucus - its quantity increases, it becomes more elastic and watery, creating favorable conditions for the penetration of sperm into the uterine cavity and protect the sperm from the high acidity of the contents of the vagina. To carry out fertilization in female reproductive tract sperm undergo physiological changes known as maturation(capacitation). When interacting with the oocyte from the sperm creates a new type of movement called hyperactive mobility.

Simultaneously, the spermatozoon undergoes morphological changes, called akrosomal reaction (acrosome reaction), namely the release of lytic enzymes and exposure patterns of sperm. As a result of these changes, sperm becomes capable to reach the egg, pass through several layers of its shell and enter into ooplazm.
Clinical examination The history of the disease
A survey of patients with infertility - it is a thorough history taking and physical examination. Necessary to determine whether the patient was ill so specific childhood diseases such as cryptorchidism, postpubertatny orchitis caused by epidemic parotitis (mumps), trauma or testicular torsion. Early puberty may indicate the adrenogenital syndrome, while the delay of sexual development - in Klinefelter syndrome or idiopathic hypogonadism. Need to clarify if there was any influence in utero, because this is accompanied by an increase in frequency of cysts of the epididymis and cryptorchism. There must be a detailed clarification of the possible impact of occupational risk factors, adverse environmental factors, excessive overheating or exposure of the body. Thus, chemotherapy of cancer has a dose-dependent and potentially devastating effect on the germ cell epithelium of the testes. Clarification is needed on whether to use drugs, potentially affecting the reproductive cycle in men: anabolic steroids, cimetidine, spironolactone. Sulfasalazine and Nitrofurantoin can affect sperm motility. Drugs and excessive use of alcohol is associated with a decrease in sperm count and hormonal disorders. Sometimes the risk of reproductive disorders may increase the pre-therapeutic and surgical diseases and their treatment. Deterioration of sperm quality observed in men with undescended testes of one. The pre-operative treatment, surgery on the neck of the bladder or the removal of retroperitoneal lymph nodes in cancer of the testicles can cause retrograde ejaculation or lack of emission. Also for retrograde ejaculation, and in some cases, impotence can result in diabetic neuropathy. When surgical treatment of groin hernias may be damaged as the spermatic cord and blood vessels in the testes. In patients with fibrosis of the bladder, usually absent deferens, seminal vesicles, an appendage of the testis. To deterioration of spermatogenesis may result any increase in temperature or general illness. At the same violations found in the ejaculate within 3 months after the event, because process of spermatogenesis from the beginning to the formation of mature sperm takes about 74 days. In addition, different period of time required for transport of spermatozoa from the tubules. Sometimes, important, even events in the previous 3-6 months.Attention should be paid to the sexual habits of people, such as the regularity of sexual activity, frequency of ejaculation, the use of special lubricants, as well as the patient's presentation about the features of ovulation cycle. Be sure to discover examined and treated if the patient previously about infertility, the reproductive function in previous marriages.
respiratory infections and infertility in men may be associated with the syndrome of ciliary dyskinesia, in which sperm is normal, but sperm are immobile due to ultrastructural defects.Kartagener syndrome - common variant of ciliary dyskinesia syndrome characterized by chronic bronchiectasis, sinusitis, situs inversus and a violation of sperm motility. When Yang syndrome, also associated with lung diseases, ultrastructure of cilia is not broken, but the outflow of sperm from the epididymis is difficult due to thickening of sperm. The examination for these patients is characterized by azoospermia. Loss of sexual desire, accompanied by headaches, visual impairment and galactorrhea may indicate a pituitary tumor. Other diseases that lead to infertility, including thyroid gland, epilepsy, diseases of the liver. Interestingly, the epilepsy itself does not cause infertility, but her usual treatment (phenytoin) affects the reproductive function. Receiving dilantina reduces the secretion of FSH. Chronic systemic diseases such as kidney disease or sickle-cell anemia accompanied reproductive hormonal disorders.
Physical examination
During the survey special attention should be paid to identify signs of hypogonadism. Typically, when viewed from this manifests itself as underdevelopment of secondary sexual characteristics, figure (span two inches more growth, the ratio of the upper body (from the highest point to pubis) to lower body (from crotch to floor), less than 1, not expressed male-pattern body hair (axillary, pubic, facial or body in combination with insufficient growth of hair at the temples)). It is also necessary to draw attention to the infantile genitalia: small sizes of the penis, testicles and prostate, and underdeveloped scrotum. In some patients, notably lack of development of muscle development and body weight.
An important phase of the survey - a thorough examination of the testes. In normal testicular size averaged 4.5 cm in length and 2.5 cm in width with an average volume of about 20 cu. see for determining the size of eggs you can use orhidometr or ruler. If the damage deferens before puberty testicles are small and tough at the time, as if damaged during adulthood reduces the size of the testes, but consistency remains soft.
A characteristic of feminization - gynecomastia. Men with congenital hypogonadism are common defects such as anosmia, cerebellar ataxia, cleft lip, uraniscochasma. Hepatomegaly may be accompanied by a violation of metabolic hormones. Inspection of the neck helps to exclude enlarged thyroid gland, vascular noises or tuberosity associated with thyroid diseases. Neurological examination necessarily includes the determination of fields of vision and reflexes.
Abnormalities of the epididymis may be the result of previous infection and possible violation of patency appendages. The examination may reveal reduction in the size of prostate in men with androgen deficiency or tenderness in the prostate infection. Must be identified any irregularities in the structure of the penis: hypospadias, curvature, phimosis. The contents of the scrotum should be carefully palpated, patients in both the vertical and horizontal positions. In many cases a simple examination of varicocele cannot see, but the survey in a standing position, or during the Valsalva maneuver, varicocele becomes noticeable. Varicocele is often the cause of reducing the size of the left testicle, so the detection of differences in the size of the right and left testicle should be the occasion for a more careful search. Should palpated both deferent duct, as about 2% of men who applied to the problem of infertility revealed congenital absence of ducts or seminal vesicles
Particular causes of infertility.
- Pathology of the hypothalamus
- Isolated gonadotropin deficiency syndrome (Kalman)
- Isolated LH deficiency ("fertile eunuch")
- Isolated FSH deficiency
- Congenital hypogonadotropism
- Pathology of pituitary
- Pituitary insufficiency (tumor, infiltrative processes, operations, radiation)
- Hyperprolactinaemia
- Hemochromatosis
- Effect of exogenous hormones (estrogen and androgen excess, an excess of glucocorticoids, hyper-and hypothyroidism)
- Pathology of the hypothalamic region
Kalman's syndrome manifested by isolated deficiency of gonadotropins (LH and FSH), occurs in the form of sporadic mutations, and in the family way. And, although the occurrence of disease is low (1 case per 10000 men), is the second after Klinefelter syndrome cause hypogonadism. Kalman's syndrome is often observed anosmia, congenital deafness, cleft lip, cleft hard palate, craniofacial asymmetry, renal dysfunction, color blindness. Hypothalamic GnRH is absent. Upon stimulation with exogenous pituitary GnRH are released LH and FSH. In addition to the deficiency of gonadotropins (LH and FSH) is a function of the anterior pituitary is not broken. Inheritance autosomal recessive or autosomal dominant with incomplete penetrance. Differential diagnosis had been delayed sexual development. A distinctive feature of the syndrome Kalman - testes size less than 2 cm in diameter and a characteristic family history in the availability of anosmia.
Fertile eunuch "Fertile eunuch" pathology associated with the isolated LH deficiency pituitary. For patients characterized figure with varying degrees of severity of virilization and gynecomastia, and large size of the testicles and reduce sperm count. The content of FSH in the blood plasma of normal, while the level and LH, and testosterone decreased. The cause of the disease in a partial deficiency of gonadotropins, which remains adequate stimulation of LH synthesis of testosterone and spermatogenesis is running, but the level of testosterone is not sufficient for the formation of secondary male sexual characteristics.
Isolated FSH deficiency is rare. Typical normal development of secondary sexual characteristics on male type, normal size of testicles and basal levels of LH and testosterone. The semen contains from 0 to a few sperm. The level of FSH in the blood plasma is low and does not respond to stimulation of GnRH.
Congenital hypogonadotropism characterized by secondary hypogonadism, and multiple somatic disorders. Prader-Willi syndrome manifested hypogonadism, muscular hypotonia in infants, and obesity. Laurence Moon Bardet Biedl syndrome inherited in an autosomal-recessive type and is characterized by mental retardation, retinitis pigmentosa, polydactyly and hypogonadism. Both syndrome associated with a violation of developing hypothalamus GnRH.
Pathology of pituitary
Pituitary insufficiency may be due to tumors, hemorrhages, be iatrogenic in nature due to surgical interventions or radiation in infiltrative processes. If dysfunction of the pituitary occur before puberty, the main clinical manifestations - a slowdown caused by insufficient adrenal and thyroid glands. Hypogonadism, found in adult men, usually develops as a result of pituitary tumors. Complaints of impotence, decreased libido, infertility may occur several years before the onset of symptoms of tumor growth (headaches, visual disturbances, reduced thyroid function, or adrenal glands). If a man has already reached normal puberty, if the disease is not associated with adrenal insufficiency requires a long period of time to disappear secondary sexual characteristics. Eventually, the eggs are soft and reduced in size. Diagnosis is based on the low level of testosterone in the blood in combination with reduced or located on the lower limit of the norm concentrations of gonadotropins.Depending on the severity of the deficiency of the pituitary in the blood plasma will be reduced levels of corticosteroids, thyroxine binding globulin, and growth hormone.
Hyperprolactinemia may be responsible for both reproductive and sexual disorders. Prolactin-secreting pituitary tumors, from microadenomy (less than 10mm) to macroadenomas, may lead to a decrease in libido, impotence, galaktoree, gynecomastia and cessation of spermatogenesis. Patients with macroadenomas generally in the first place of palpation complaint
violation of the fields of vision and headaches. In this situation it is necessary examinations, including CT or MRI scan of the pituitary, laboratory determination of hormones of the anterior pituitary, thyroid and adrenal glands. These patients indicated a decreased level of testosterone in the blood decrease or trends to the bottom of LH and FSH standards, reflecting the inadequate response of the hypophysis to reduce production of testosterone.
About 80% of male patients with hemochromatosis have testicular dysfunction. These patients may develop secondary hypogonadism in the background deposition of iron in the liver or may be primary, resulting in deposition of iron in the testes tissue. Iron deposition in hemochromatosis also detected in the pituitary gland, making the main source of pituitary disorders.
Regarding the role of exogenous hormones, the adrenal tumors, Sertoli cells, interstitial cells of the testes can produce estrogens. Cirrhosis of the liver accompanied by an increase of endogenous estrogens. First, estrogen suppresses the secretion of pituitary gonadotropins, and as a result of the development of secondary testicular failure. Androgens can also suppress the secretion of pituitary gonadotropins and promote the development of secondary testicular failure. Some athletes use anabolic steroids may lead to temporary infertility. Increased formation of endogenous androgens may occur as a result of androgen-producing adrenal tumors, testicular tumors, but the most common cause - congenital adrenal hyperplasia. In CAH increased formation of androgens adrenal cortex, leading to premature puberty and abnormally large size of the penis. Since the secretion of gonadotropins is suppressed, the testicles are not mature and have small sizes. In the absence of premature puberty diagnosis is extremely difficult, because the excess virilization difficult to distinguish from the normal sexually mature male.Need for a thorough laboratory examination. In diagnostically prescribed cases CAH infertility treatment is carried out using corticosteroids.Often physicians use corticosteroids in cases of idiopathic infertility. However, if during the survey cause of the violations do not have such therapy should not be used.
Sometimes, excessive use of glucocorticoids in the treatment of ulcerative colitis, asthma, rheumatoid arthritis leads to a decrease in spermatogenesis. Possible cause secondary testicular dysfunction - the suppression of LH secretion increased levels of plasma cortisol.Correction of an excess of glucocorticoids is accompanied by improvement of spermatogenesis.
Disruption of spermatogenesis may be due to malfunction of the thyroid gland. Hyper-and hypothyroidism can affect spermatogenesis.Hyperthyroidisim affects both the work of the pituitary, and in the testes, modifying the secretion of releasing hormones, and activating the conversion of androgens into estrogens in peripheral tissues.
Testicular causes of infertility
- Chromosomal abnormalities
- (Klinefelter syndrome, XX syndrome (syndrome of sexual reversion), XYY syndrome)
- Noonan's syndrome (a male version of Turner's syndrome)
- Myotonic dystrophy
- Bilateral anorchidism syndrome (absence of testes)
- Syndrome of the presence of only Sertoli cells (germ cell aplasia epithelium)
- Effect (drugs, radiation)
- Orchitis
- Injury
- Systemic diseases
(Renal failure, liver disease, sickle-cell anemia)
- Violations of the synthesis or the effect of androgens
- Cryptorchidism
- Varicocele
A number of anomalies in the structure of somatic chromosomes associated with male infertility. Examination of 1263 couples who applied to the problem of infertility, 6.2% of men were found chromosomal abnormalities. In a subgroup with decreased sperm count below 10 million / ml, the percentage of occurrence of chromosome abnormalities in males increased to 11% and in men with azoospermia the frequency of chromosome abnormalities was 21%. However, only in rare cases to confirm the relationship of infertility with specific chromosomal aberration, as DD translocation, ring chromosomes, reciprocal translocations and other aberrations. Nevertheless, to avoid anomalies of somatic and sex chromosomes in males with severe oligospermia or azoospermia should be conducted cytogenetic examination.
Klinefelter's syndrome - a genetic disorder associated with the presence of men more X-chromosome. It is dominated by two types of karyotype: 47XXY (classical form syndrome), or 46 XY/47XXY (mosaicism). The prevalence of the disease among men about 1:500. For these patients is characterized by dense, small testes, delayed sexual development, azoospermia, gynecomastia. Due to the fact that before puberty the characteristic signs of hypogonadism is not obvious, the diagnosis is usually established late. Reducing the size of the testicles usually occurs as a result of sclerosis of tubules. Typical sizes of eggs less than 2 cm in length and volume of less than 12 cm3.Characterized by increasing levels of LH and FSH. The level of testosterone varies from normal to reduced and decreases with age. The level of estradiol in the blood is usually elevated. Higher compared with the testosterone levels of estrogen lead to a feminization in the form of gynecomastia. Approximately 10% of these patients have chromosomal mosaicism. In these cases, the characteristic features of Klinefelter syndrome are less pronounced and men can be fertile in the event that there is a clone of a testicular cells containing normal set of chromosomes. Moderate dementia, restrictive lung pathology is encountered in these patients more frequently than in the population. Infertility in these patients is reversible and later the majority required replacement therapy with androgens in order to achieve optimal virilization and normal sexual function.
XX - violation or syndrome sex reversal
Klinefelter syndrome. Clinical symptoms are similar, except for below-average growth and hypospadias; cases of mental disability are less common. Patients have the karyotype 46HH. This paradox is explained by expression on cells of H-Y antigen and presumably the presence of the genome structures of Y-chromosome.
The frequency of XYY syndrome is approximately equal to the frequency of Klinefelter syndrome. Phenotypic manifestations of XYY syndrome are similar to Klinefelter syndrome, but more variable. Indicators of sperm in these men vary from normal to azoospermia. For patients, characterized by excessively high growth and acne, in a high percentage of cases observed antisocial behavior. The level of LH and testosterone levels in most patients is normal, and the level of FSH depends on the degree of damage to germ cells. Treatment of infertility does not exist.
Noonan's syndrome - male version
Turner syndrome (XO), and patients characterized by similar symptoms: small stature, wing folds on the neck, low-set ears, cubitus Valgus, visual disturbances and malformations of the cardiovascular system. Most men with Noonan syndrome occurs cryptorchidism, reduction of spermatogenesis and infertility. By reducing the function of testicular LH and FSH levels in the blood increased. Conducting cytogenetic survey reveals violations of sex chromosomes, such as mosaicism XO / XY. Treatments of infertility in these patients does not exist.
In patients with myotonic dystrophy observed violation of muscle relaxation after the initial reduction. The main clinical manifestations also include cataract, frontal baldness and testicular atrophy. The disease is inherited in an autosomal-dominant type and its manifestations are variable. .
Puberty usually occurs without singularities, and damage to the testicles develop later in adulthood. The function Leydig cells remains normal and gynecomastia is not observed.
Bilateral anorchidism or absence of the testes syndrome is very rare, approximately 1:20000 men. In these patients the testicles at birth are not defined and later, due to lack of synthesis of androgens in the testes, develops sexual immaturity. Karyotype of the patient are normal; LH and FSH levels increased and testosterone levels are very low. During the intrauterine period of development of the testes may be lost as a functioning organ trauma, torsion, vascular injury or infection. Nevertheless, in order to occur differentiation of the reproductive system of male type, functioning tissue testes should be present at least during the first trimester prenatal period. In response to hCG stimulation of testosterone does not increase. For patients characterized thin physique. Gynecomastia is not typical. In the course of treatment is only possible correction of deficiency of testosterone. Treatments of infertility in these patients does not exist.
Syndrome of the presence of only Sertoli cells or germ cell aplasia of the epithelium, may be due to different causes: congenital absence of germ cell epithelium, genetic defects, resistance to androgens. When testicular biopsy revealed a complete absence of germinal epithelium, and clinical examination azoospermia in conjunction with normal virilization, testicular consistency was normal, but their size somewhat reduced, gynecomastia does not. Testosterone and LH in normal, but FSH levels are usually elevated. Sometimes patients with other diseases testes (mumps, cryptorchidism, damage from radiation and toxic exposure), seminiferous tubules may also contain only Sertoli cells, but these patients will be reduced testes size, and histological examination of the material is uneven. As the characteristic features of these patients more frequently observed sclerosis and hyalinosis. Infertility treatment is not effective.
drugs and radiation may have a damaging effect on the germ cell epithelium, because germ cell epithelium - a rapidly dividing tissue, and the process of cell division is most sensitive to the damaging effects. Chemotherapy of cancer has a dose-dependent effect on the germ cell epithelium. In the period preceding the sexual maturation of germinal epithelium of the testes is more resistant to the toxic effects of drugs than in adulthood. Alkylating drugs used in chemotherapy, such as hiromantin, cyclophosphamide toxicity have damaging effect on the testes. A number of patients before chemotherapy may conduct cryopreservation of sperm. Cyproterone, ketoconazole, spironolactone, alcohol contribute to disruption of synthesis of testosterone. Cimetidine - testosterone antagonist, blocks the peripheral action of testosterone in target-tissues. Frequent side effects - gynaecomastia and reduced sperm count. Narcotic drugs such as marijuana, heroine, methadone leads to a lower level of testosterone in plasma, without a concomitant increase LH. This indicates that both the violation of central origin, and violations at the level of the testes. Discovered weakening testicular function under the influence of some pesticides, for example, dibromohlorpropana. Particularly sensitive to radiation, germ cell epithelium, while Leydig cells are relatively stable. Irradiation with a dose of less than 600 rad leads to a reversible cell damage eggs. At higher levels of exposure are more likely occurrence of persistent violations.Recovery of spermatogenesis may take 2-3 years even in men who have undergone low doses of radiation. Elevated levels of FSH reflects a weakening of spermatogenesis. When restoring testicular function of FSH levels returned to normal.
In 15-20% of adult men mumps can lead to the development of orchitis, usually unilateral. Bilateral orchitis occurs in about 10% of cases.Within 1 to 6 months, or within a few years after the disease may develop testicular atrophy. Normal rates of sperm recovered less than 1 / 3 of men.
Such systemic diseases such as renal failure, accompanied by a male decreased libido, impotence, a violation of spermatogenesis, gynecomastia. LH and FSH levels increased, and testosterone levels decreased. The cause of hypogonadism in uremia multifactorial. Every fourth patient with uremia found elevated prolactin levels. Additional contributions can make an excess of estrogen. Antihypertensive drugs, uremic neuropathy may also play a role in the development of impotence and hypogonadism. After successful kidney transplantation for uremic hypogonadism improves. In a large percentage of men with liver cirrhosis observed testicular atrophy, impotence, and gynecomastia.Testosterone reduced, while the level of estradiol increased due to the simultaneous decrease in the synthesis of androgens in the liver and increase the peripheral conversion to estrogens. At relatively low levels of serum testosterone observed a moderate increase in LH and FSH.Also, to reduce blood levels of testosterone causes alcohol, due to suppression of testosterone synthesis in the testes. For the majority of men with sickle cell anemia is characterized by symptoms of hypogonadism. Although LH and FSH levels may be different levels of testosterone decreased. Hypogonadism with sickle-cell anemia may develop secondary to the testicular and hypothalamic-pituitary disorders.
Rare inherited disorders of enzymes involved in the synthesis of testosterone, accompanied inadequate virilization, to be seen at birth in the form of hermaphroditism. Some forms of androgen resistance leads to a lack of virilization, infertility and the development of male sexual characteristics of female type. Diagnosis is based on the detection of abnormal androgen receptors in skin fibroblast culture genitals.Interestingly, the level of testosterone and LH increased. Diagnosis of these disorders is expensive, but effective treatments for infertility does not exist.
Cryptorchidism occurs in 0.8% of adult men. Morphological changes in the retained testis begin to develop after 2 years of age. Despite prophylactic holding, patients suffering from unilateral cryptorchidism have reduced fertility potential. Especially strongly disturbed sperm quality in men with bilateral undescended testes. Although basal levels of LH, FSH and testosterone may be normal, LH and FSH response to GnRH stimulation elevated, which may reflect a violation of testicular function.
Varicocele scrotum - one of the most frequent findings in men who have addressed the problem of infertility. The cause of varicocele - violation outflow of blood due to deficiency or absence of valves seminal veins. Such a defect in the valve apparatus in combination with the long vertical course of the internal spermatic vein on the left leads to more frequent formation shift to the left varicocele (90% of). Internal seminal Vienna has a right oblique stroke, and therefore the right varicocele is usually not determined. The appearance of a unilateral, located right varicocele may be a consequence of venous thrombosis, tumors or in situ inversus. Studies using modern diagnostic techniques show the occurrence of bilateral varicocele in more than 40% of cases. Among men the prevalence of varicocele is approximately 21%, and a group of men suffering from infertility, this figure increases to 40%. Approximately 50% of men with varicocele revealed deterioration of sperm quality, although it is also many men fertility of sperm stored. The following assumptions mechanisms violation of spermatogenesis in men with varicocele:
- Increasing the temperature in the testicles due to venous stasis
- Retrograde flow of toxic metabolites from the adrenal glands and kidneys
- Stagnation of blood with the development of hypoxia germ cell epithelium, and
- Changes in the functioning of the hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular axis
These recent experimental results confirm investigates the connections between increased blood flow, raising the temperature in the testes and disruption of spermatogenesis.
Unfortunately, 25-40% of men with infertility are diagnosed with idiopathic male infertility when the cause cannot be established. With the advancement of our knowledge about the physiology of the male reproductive system of a group of patients with unexplained infertility will gradually decrease.
post testicular infertility
Disorders of sperm transport
Congenital
Acquired violation
Functional disturbances
Violations of mobility or function of sperm
Congenital malformations of the sperm tail
Violation of sperm maturation
Immunological disorders
Infections
Sexual dysfunction
Violations of the transport of sperm
Congenital anomalies of sperm transport are rare and are caused by the absence or atresia tubular sections of the male reproductive tract. In men with fibrosis of the bladder increased frequency of congenital hypoplasia or absence of the main body of the epididymis, spermatic cord and seminal vesicles. The absence of seminal vesicles is always accompanied by azoospermia, a violation of coagulation of semen during ejaculation, and lack of fructose in semen. Young's syndrome associated with pulmonary pathology, ultrastructure of the cilia is normal, but the outflow of sperm from the epididymis is difficult due to thickening of sperm that leads to azoospermia.
Acquired violations transport of sperm, usually associated with bacterial infections that lead to the development of acute or chronic inflammation in the epididymis, with subsequent formation of scar tissue and obstruction. In addition to vasectomy, random ligation of spermatic cord is possible with surgical treatment of inguinal hernias, and even during varicostomy.
Functional obstruction of sperm transport is the result of innervation in the sympathetic nerve injury during surgical removal of retroperitoneal lymph nodes are located, or in operations on the pelvic organs. Innervation may cause the insufficient reduction of spermatic cord with subsequent failure of issue, as well as violation of reducing the bladder neck during ejaculation and, as a consequence - retrograde ejaculation. Damage to the spinal cord can lead to para-and tetraplegia, followed by erectile dysfunction and a violation of emission and ejaculation. Disrupt the sympathetic nervous system may be many medications such as tranquilizers, antidepressants, antihypertensive drugs.
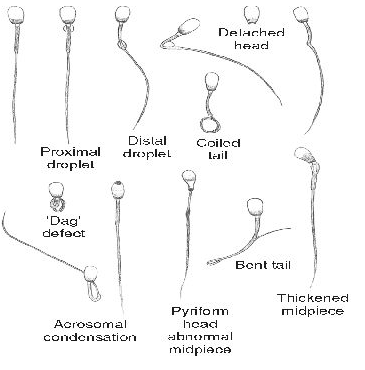
Violation of mobility and function of sperm
Violation of mobility and function of sperm develops secondarily as a result of congenital defects of the sperm tail, disrupting the maturation of sperm, immunological disorders.
Ciliary dyskinesia syndrome - a group of diseases characterized by immobility, a deterioration of sperm motility, such as Kartagener syndrome. In these diseases results in normal testicular biopsy, sperm count in the fracture normal, but sperm motility or significantly reduced, or sperm immobile. Ultrastructural defects, leading to disability as cilia and sperm, can be seen only by electron microscopy. The defects underlying the ciliary dyskinesia syndrome, include the lack of dineinovyh pens, short or absent radial connection without a central cover and lack of central microtubules. Violation of sperm motility Mauger also be due to the lack of protein in sperm tail.
The normal number but reduced motility may occur after vasectomy due to dysfunction epididymis. Chronic increase internal pressure that occurs after vasectomy, can have a negative effect on the epididymis - sperm cannot pass the normal stages of maturation and acquire mobility. Violation gamato-testicular barrier as a result of infection, trauma or surgery is accompanied by sensitization of the organism with antigens of spermatozoa. Antisperm antibodies play a role in the development of infertility in 3-7% of infertile men. Immune disorders are usually not the absolute cause of infertility in the patient, but can reduce the fertility of sperm.
Infections. High concentrations of gram-negative bacteria such as E. coli, in the sperm can reduce sperm motility. Urogenital infections such as chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis, rarely cause infertility. Studies in both animals and humans have not produced convincing evidence to support the need for bacteriological culture or empirical antimicrobial therapy in asymptomatic infertile men.
Sexual dysfunction was observed in 20% of infertile men. Reduced sexual desire, erectile dysfunction, premature ejaculation – potential cause reproductive failure. Reduced libido and erectile dysfunction can be due to low testosterone levels associated with organic pathology.
Diagnostic tests & Sperm Counts
Despite the fact that semen analysis is not a test for fertility, careful study to evaluate the functional state of hormonal regulation, spermatogenesis and the patency of the reproductive tract. The only true indicator of fertility - is pregnancy and this phenomenon is associated with the state of the couple as a whole. It must be borne in mind that the boundaries of normal values of sperm is difficult to determine in healthy men in their reproductive period. Clinical studies of patients with infertility have allowed to establish "normal ranges", below which the chances of pregnancy reduced. These boundaries are not absolute, because some fertile male semen parameters may be below the limit of normal. Conversely, men who addressed the problem of infertility in the standard survey methods may have had normal sperm, because the standard survey does not assess the functional ability of sperm. In the conduct of sperm is strongly recommended to use the "Laboratory guide to the analysis of human sperm and the interaction between sperm from the cervix, the World Health Organization (WHO). Most experts are exploring at least three semen samples, indicators of which differ from each other within 20%, before the conclusion about the state of the sperm. To analyze the best use of a sample of sperm obtained by masturbation after 2-3 days abstinence from sexual activity. The study sample should be held within 1-2 hours after receipt. Also for the analysis is possible, but less desirable to use samples of semen obtained by coitus interruptus or silicone condom that does not contain spermicides. Therefore, it is best if the samples of sperm are obtained directly from the venue of the study. In addition to the errors in the conduct of research in the laboratory, in different samples of semen obtained from the same man, indicators such as density, motility and morphology of spermatozoa may vary. In many respects, such a variation of indicators affects the long period of abstinence. With each additional day of abstinence (up to 1 week) increases the amount of seed to 0.4 ml, sperm concentration of 10-15 million, and total sperm count 50-90 million sperm motility and morphology does not change over the next 5-7 days abstinence but longer term a decline of sperm motility. Interpreting the results of semen analysis should take into account the differences between the different samples.
About 15% of couples trying to get pregnant the first time fail. Most doctors make a diagnosis of primary infertility in cases where pregnancy does not occur within one year of regular sexual life without contraception.

According to statistics from 80-85% of couples conceiving occurs within 12 months of sexual activity without contraception, and situations where the pregnancy during this period of time not come, considered as a possible infertility, and patients should test. Data from the past 20 years show that approximately 30% of cases of problems with conception plays a role only male factor, and approximately 20% of the violations found both the husband and his wife.

Thus, male factor, at least in part, plays a role in 50% cases of infertility.
Major problems with identifying male factor infertility related to timing of the test, the most effective scheme of examination of men and the most rational forms of therapy and operative treatment methods. In solving the problem of infertility is extremely important to consider the couple as a unit to allow the simultaneous screening and treatment of both spouses. The longer the period of infertility, the lower the chances of a married couple to achieve a positive result. Many families are beginning to experience after several months of non-occurrence of pregnancy. In such cases, should not be encouraged to continue to expect a pregnancy without her husband's study. The initial stages of the survey men should be held whenever the patients treated with the main complaint of infertility. Such a survey should be quick, noninvasive and inexpensive.
Reproductive physiology of men. The axis of the hypothalamus
The hypothalamus - the main integrative center functional reproductive system in men. Receiving information from the central nervous system and testes, hypothalamus regulates the formation and secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). Neurotransmitters and neuropetides have both inhibitory and stimulating effect on the hypothalamus. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), secreted by the hypothalamus in a pulsating mode, which is a necessary step stimulation of synthesis and secretion of both gonadotropins pituitary (LH and FSH). It is interesting and ironic that the appointment of GnRH is not in the momentum, and in continuous operation results after the initial stimulation of pituitary gonadotropin release of the oppression of the allocation of LH and FSH. And luteinizing (LH) and follicle-stimulating (FSH), a hormone produced in the anterior lobe of the pituitary and secreted in a pulse mode in response to a pulsating production of GnRH. In the testes, LH and FSH bind to specific receptors on the Leydig cells and Sertoli. Testosterone, the main product of the internal secretion of the testis, is the main inhibitor of secretion of luteinizing hormone in men. In the peripheral tissues of testosterone can be converted into more potent androgen dihydrotestosterone, or a powerful estrogen - estradiol. Androgens and estrogens are formed independently regulate the secretion of LH.
Production of FSH is regulated by the mechanism of feedback of inhibion, formed in the Sertoli cells. The deterioration of spermatogenesis is accompanied by a decrease in formation and as a consequence (according to the mechanism of negative feedback) increased secretion of FSH. Isolated increase in FSH levels - an important marker of the state of germ cell epithelium of the testes.
Secretion of prolactin also has a complicated relationship with gonadotropic hormone. In men with hyperprolactinemia increased level of prolactin has an inhibitory effect on the secretion of GnRH. In addition to the suppression of secretion of LH and testosterone production increase in prolactin levels may have a direct impact on the central nervous system. In men with hyperprolactinemia receiving substitution therapy with testosterone, libido and sexual function were not restored until then, until a decrease in the level of prolactin.
Testicles. Leydig cells.
Testosterone is secreted in a pulsating mode of Leydig cells in response to the pulsating secretion of LH. For testosterone circadian rhythm of secretion, with peak secretion in the early morning and decreasing in the afternoon or evening.

In the intact egg after the exogenous administration of a number of LH receptors to LH in the testes is reduced as a result of Down-regulation. High doses of GnRH and its analogs may lead to a decrease in the number of LH receptors and thus suppress the secretion of LH. In practice, this feature is used to pharmacological castration in men with prostate cancer. Estrogens inhibit the activity of several enzymes involved in the synthesis of testosterone, and thus directly affect the formation of testosterone. There is also a inside ultra short feedback loop through which exogenous testosterone will override the effect of LH and inhibit production of endogenous testosterone. In healthy men, only 2% of circulating testosterone in the blood is in free or unbound state, 44% of testosterone associated with testosterone-estradiol-binding globulin (sex steroids globulin, SHBG), and 54% albumin or other proteins. These steroid proteins modulate the action of androgens. SHBG has a higher affinity for testosterone than for estradiol, and changes in SHBG levels leads to changes in hormonal levels. The level of SHBG is increased under the influence of estrogen in the treatment of thyroid hormones, liver cirrhosis, and may decline under the influence of androgens, growth hormone and obesity. The biological action of androgens appears to target-organs that contain specific protein receptors to androgen. Testosterone from the circulating blood enters the target cell, where under the influence of the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase into a more powerful androgen-dihydrotestosterone. The main effects of androgens in target-tissues include:
- Regulation of gonadotropin secretion of the hypothalamic-pituitary system;
- Initiation and maintenance of spermatogenesis;
- Differentiation of internal and external genitalia during fetal development;
- Promotion of sexual development at puberty.
Seminiferous tubules

Seminiferous tubules contain germ cells of the epithelium at different stages of maturation and their supporting Sertoli cells. Seminiferous tubules are up 85-90% of the testes. Sertoli cells represent a permanent population of nondividing cells microenvironment. They are located on the basement membrane of seminiferous tubules and are connected by dense formations (tight junctions). These dense connections with closely interconnected muscle cells peritubular space form hemato-testicular barrier. Functional significance of the hemato-testicular barrier is to create a unique microenvironment necessary for spermatogenesis, and maintenance of immune privilege of testis. This insulation is very important, because education is sperm puberty, which is much later serve as the immune system. If the formation of sperm was not immunologically protected, then the differential cells would be recognized, the immune system as foreign and destroyed would. Sertoli cells are involved, how to feed the developing sperm cells, and in the phagocytosis of dead cells. Spermatogonia and young spermatocytes located in the seminiferous tubules near the basal membrane and the maturing move in a more upper layers deep into the lumen of the tubules.
Germinal or spermatogenic, the cells are located in the seminiferous strictly defined way. Spermatogonia lie directly on the basement membrane and in the direction of the lumen of the tubules are arranged in series-WIDE primary spermatocytes, secondary spermatocytes and spermatids. Revealed 13 different types of germ cells of the epithelium, representing different stages of maturation of sperm.
Spermatogenesis

Spermatogenesis

A complex process in which the primitive germ cells or spermatogonia, divide, reproducing like a stem cell, or give rise to daughter cells subsequently differentiate into spermatocytes. Further division of spermatocytes gives rise to lines of cells that eventually differentiate into spermatids and further into sperm. Differentiation involves the condensation of the nucleus, acrosome formation, and loss of much of the cytoplasm, the formation of the tail and movement of mitochondria in the middle part of the sperm, which becomes the "engine room" cells, providing job tail. With germ cells of the epithelium, while getting into the processes of spermatogenesis, called a generation. The cells of one generation are on the same stage of development.
Six developmental stages of germ cell epithelium.

The development of sperm from the first stage to the sixth of a cycle. In humans, the duration of each cycle of approximately 16 days, but the way the transformation from early spermatogonia to mature sperm takes 4.6 cycles. Thus, the duration of spermatogenesis in humans is about 74 days.
Hormonal regulation of spermatogenesis
Between the two separate parts of the testis - seminiferous, and Environ-mental to the interstitial tissue - there is a close structural and functional relationship. Luteinizing hormone pituitary affect spermatogenesis indirectly by stimulating the production of testosterone. Target cells of FSH - Sertoli cells. Thus, FSH and testosterone - hormones that directly affect the epithelium of the seminiferous tubules. Androgen type protein formed Sertoli cells and involved in intracellular transport of testosterone, may play a role of testosterone in the reservoir tubules in addition to testosterone coming from the testicular tubules in the epididymis. A close relative position of Leydig cells and seminiferous tubules, as well as the formation of Sertoli cells of androgen-binding globulin, maintains a high concentration of testosterone in the microenvironment of differentiating cells of spermatogenesis. Hormonal changes needed to run spermatogenesis occur regardless of the process of maintaining spermatogenesis. In order to maintain spermatogenesis, for example, by turning off the pituitary gland, is necessary only testosterone. However, if the function of germ cell epithelium off in a lack of testosterone, then run spermatogenesis requires both FSH and testosterone.
Transport - maturation - Storage of sperm

Although, the formation of spermatozoa takes place in the egg, the processes of maturation, storage and transport of sperm provided by the epididymis (epididymis). Spermatozoa that are in seminiferous testis are immobile and incapable of fertilization. Their maturation is completed outside the egg in the ducts of the epididymis. Tortuous seminiferous tubules testicular end network testis, which in turn forms the efferent ducts (ductuli efferentes). These efferent tubules of testicular fluid and sperm come from eggs in the epididymis head. Parorchis or epididymis has a head, body and tail and consists of a single, highly twisted duct whose length is about 5-6 meters. Although the duration of transport in the stream epididymis varies depending on age and sexual activity of men, on average, this time is 4 days. In that period of maturation in the head and body of the epididymis sperm are becoming increasing mobility and the ability to fertilize an egg.

In addition to the maturation of sperm, testicular appendage acts as a "storage" or reservoir of male germ cells. It is estimated that the reservoir semen contains about 440 million sperm, more than 50% of which lies in the caudal part of epididymis. From the tail of the epididymis sperm enter the spermatic cord (vas deferens), which is a muscular tube length 30-35cm. The contents of spermatic cord through the peristaltic reductions wall duct enters semi basal channel (ductus ejaculatorius) and then through the emission and ejaculation in the urethra. During the emission of the secret of the seminal vesicles and prostate gland goes into the posterior urethra. Ejaculatory duct reduction and muscles of the bladder neck under the control of the sympathetic nervous system.
During ejaculation, the bladder neck muscles contracting and relaxing external sphincter, and the sperm moves from the urethra by rhythmic reductions perineal and bulbourethral muscles. It is established that the first portion of the ejaculate contains a small amount of fluid from the spermatic cord, but contains a large number of spermatozoa. The bulk of seminal fluid produced in the seminal vesicle and to a lesser extent - in the prostate. The seminal vesicles provide a nutritious substrate sperm - fructose, as well as prostaglandins and coagulating substance. An established function of seminal plasma is to create a buffer in the acidic environment vagina. Clot formed sperm after ejaculation, liquefies within 20-30 minutes under the influence of proteolytic enzymes of the prostate. Secret of the prostate also adds to the seminal fluid zinc ions, phospholipids, spermine, phosphatase. The first portion of ejaculate is characterized by a maximum content of sperm and secretion of the prostate, while the second portion is represented, first of all, the secret of the seminal vesicles and contains fewer sperm.
Fertilization
Typically, fertilization occurs in the fallopian tubes during ovulation. In per ovulatory period (in the middle of the menstrual cycle) is changing the cervical mucus - its quantity increases, it becomes more elastic and watery, creating favorable conditions for the penetration of sperm into the uterine cavity and protect the sperm from the high acidity of the contents of the vagina. To carry out fertilization in female reproductive tract sperm undergo physiological changes known as maturation(capacitation). When interacting with the oocyte from the sperm creates a new type of movement called hyperactive mobility.

Simultaneously, the spermatozoon undergoes morphological changes, called akrosomal reaction (acrosome reaction), namely the release of lytic enzymes and exposure patterns of sperm. As a result of these changes, sperm becomes capable to reach the egg, pass through several layers of its shell and enter into ooplazm.
Clinical examination The history of the disease
A survey of patients with infertility - it is a thorough history taking and physical examination. Necessary to determine whether the patient was ill so specific childhood diseases such as cryptorchidism, postpubertatny orchitis caused by epidemic parotitis (mumps), trauma or testicular torsion. Early puberty may indicate the adrenogenital syndrome, while the delay of sexual development - in Klinefelter syndrome or idiopathic hypogonadism. Need to clarify if there was any influence in utero, because this is accompanied by an increase in frequency of cysts of the epididymis and cryptorchism. There must be a detailed clarification of the possible impact of occupational risk factors, adverse environmental factors, excessive overheating or exposure of the body. Thus, chemotherapy of cancer has a dose-dependent and potentially devastating effect on the germ cell epithelium of the testes. Clarification is needed on whether to use drugs, potentially affecting the reproductive cycle in men: anabolic steroids, cimetidine, spironolactone. Sulfasalazine and Nitrofurantoin can affect sperm motility. Drugs and excessive use of alcohol is associated with a decrease in sperm count and hormonal disorders. Sometimes the risk of reproductive disorders may increase the pre-therapeutic and surgical diseases and their treatment. Deterioration of sperm quality observed in men with undescended testes of one. The pre-operative treatment, surgery on the neck of the bladder or the removal of retroperitoneal lymph nodes in cancer of the testicles can cause retrograde ejaculation or lack of emission. Also for retrograde ejaculation, and in some cases, impotence can result in diabetic neuropathy. When surgical treatment of groin hernias may be damaged as the spermatic cord and blood vessels in the testes. In patients with fibrosis of the bladder, usually absent deferens, seminal vesicles, an appendage of the testis. To deterioration of spermatogenesis may result any increase in temperature or general illness. At the same violations found in the ejaculate within 3 months after the event, because process of spermatogenesis from the beginning to the formation of mature sperm takes about 74 days. In addition, different period of time required for transport of spermatozoa from the tubules. Sometimes, important, even events in the previous 3-6 months.Attention should be paid to the sexual habits of people, such as the regularity of sexual activity, frequency of ejaculation, the use of special lubricants, as well as the patient's presentation about the features of ovulation cycle. Be sure to discover examined and treated if the patient previously about infertility, the reproductive function in previous marriages.
respiratory infections and infertility in men may be associated with the syndrome of ciliary dyskinesia, in which sperm is normal, but sperm are immobile due to ultrastructural defects.Kartagener syndrome - common variant of ciliary dyskinesia syndrome characterized by chronic bronchiectasis, sinusitis, situs inversus and a violation of sperm motility. When Yang syndrome, also associated with lung diseases, ultrastructure of cilia is not broken, but the outflow of sperm from the epididymis is difficult due to thickening of sperm. The examination for these patients is characterized by azoospermia. Loss of sexual desire, accompanied by headaches, visual impairment and galactorrhea may indicate a pituitary tumor. Other diseases that lead to infertility, including thyroid gland, epilepsy, diseases of the liver. Interestingly, the epilepsy itself does not cause infertility, but her usual treatment (phenytoin) affects the reproductive function. Receiving dilantina reduces the secretion of FSH. Chronic systemic diseases such as kidney disease or sickle-cell anemia accompanied reproductive hormonal disorders.
Physical examination
During the survey special attention should be paid to identify signs of hypogonadism. Typically, when viewed from this manifests itself as underdevelopment of secondary sexual characteristics, figure (span two inches more growth, the ratio of the upper body (from the highest point to pubis) to lower body (from crotch to floor), less than 1, not expressed male-pattern body hair (axillary, pubic, facial or body in combination with insufficient growth of hair at the temples)). It is also necessary to draw attention to the infantile genitalia: small sizes of the penis, testicles and prostate, and underdeveloped scrotum. In some patients, notably lack of development of muscle development and body weight.
An important phase of the survey - a thorough examination of the testes. In normal testicular size averaged 4.5 cm in length and 2.5 cm in width with an average volume of about 20 cu. see for determining the size of eggs you can use orhidometr or ruler. If the damage deferens before puberty testicles are small and tough at the time, as if damaged during adulthood reduces the size of the testes, but consistency remains soft.
A characteristic of feminization - gynecomastia. Men with congenital hypogonadism are common defects such as anosmia, cerebellar ataxia, cleft lip, uraniscochasma. Hepatomegaly may be accompanied by a violation of metabolic hormones. Inspection of the neck helps to exclude enlarged thyroid gland, vascular noises or tuberosity associated with thyroid diseases. Neurological examination necessarily includes the determination of fields of vision and reflexes.
Abnormalities of the epididymis may be the result of previous infection and possible violation of patency appendages. The examination may reveal reduction in the size of prostate in men with androgen deficiency or tenderness in the prostate infection. Must be identified any irregularities in the structure of the penis: hypospadias, curvature, phimosis. The contents of the scrotum should be carefully palpated, patients in both the vertical and horizontal positions. In many cases a simple examination of varicocele cannot see, but the survey in a standing position, or during the Valsalva maneuver, varicocele becomes noticeable. Varicocele is often the cause of reducing the size of the left testicle, so the detection of differences in the size of the right and left testicle should be the occasion for a more careful search. Should palpated both deferent duct, as about 2% of men who applied to the problem of infertility revealed congenital absence of ducts or seminal vesicles
Particular causes of infertility.
- Pathology of the hypothalamus
- Isolated gonadotropin deficiency syndrome (Kalman)
- Isolated LH deficiency ("fertile eunuch")
- Isolated FSH deficiency
- Congenital hypogonadotropism
- Pathology of pituitary
- Pituitary insufficiency (tumor, infiltrative processes, operations, radiation)
- Hyperprolactinaemia
- Hemochromatosis
- Effect of exogenous hormones (estrogen and androgen excess, an excess of glucocorticoids, hyper-and hypothyroidism)
- Pathology of the hypothalamic region
Kalman's syndrome manifested by isolated deficiency of gonadotropins (LH and FSH), occurs in the form of sporadic mutations, and in the family way. And, although the occurrence of disease is low (1 case per 10000 men), is the second after Klinefelter syndrome cause hypogonadism. Kalman's syndrome is often observed anosmia, congenital deafness, cleft lip, cleft hard palate, craniofacial asymmetry, renal dysfunction, color blindness. Hypothalamic GnRH is absent. Upon stimulation with exogenous pituitary GnRH are released LH and FSH. In addition to the deficiency of gonadotropins (LH and FSH) is a function of the anterior pituitary is not broken. Inheritance autosomal recessive or autosomal dominant with incomplete penetrance. Differential diagnosis had been delayed sexual development. A distinctive feature of the syndrome Kalman - testes size less than 2 cm in diameter and a characteristic family history in the availability of anosmia.
Fertile eunuch "Fertile eunuch" pathology associated with the isolated LH deficiency pituitary. For patients characterized figure with varying degrees of severity of virilization and gynecomastia, and large size of the testicles and reduce sperm count. The content of FSH in the blood plasma of normal, while the level and LH, and testosterone decreased. The cause of the disease in a partial deficiency of gonadotropins, which remains adequate stimulation of LH synthesis of testosterone and spermatogenesis is running, but the level of testosterone is not sufficient for the formation of secondary male sexual characteristics.
Isolated FSH deficiency is rare. Typical normal development of secondary sexual characteristics on male type, normal size of testicles and basal levels of LH and testosterone. The semen contains from 0 to a few sperm. The level of FSH in the blood plasma is low and does not respond to stimulation of GnRH.
Congenital hypogonadotropism characterized by secondary hypogonadism, and multiple somatic disorders. Prader-Willi syndrome manifested hypogonadism, muscular hypotonia in infants, and obesity. Laurence Moon Bardet Biedl syndrome inherited in an autosomal-recessive type and is characterized by mental retardation, retinitis pigmentosa, polydactyly and hypogonadism. Both syndrome associated with a violation of developing hypothalamus GnRH.
Pathology of pituitary
Pituitary insufficiency may be due to tumors, hemorrhages, be iatrogenic in nature due to surgical interventions or radiation in infiltrative processes. If dysfunction of the pituitary occur before puberty, the main clinical manifestations - a slowdown caused by insufficient adrenal and thyroid glands. Hypogonadism, found in adult men, usually develops as a result of pituitary tumors. Complaints of impotence, decreased libido, infertility may occur several years before the onset of symptoms of tumor growth (headaches, visual disturbances, reduced thyroid function, or adrenal glands). If a man has already reached normal puberty, if the disease is not associated with adrenal insufficiency requires a long period of time to disappear secondary sexual characteristics. Eventually, the eggs are soft and reduced in size. Diagnosis is based on the low level of testosterone in the blood in combination with reduced or located on the lower limit of the norm concentrations of gonadotropins.Depending on the severity of the deficiency of the pituitary in the blood plasma will be reduced levels of corticosteroids, thyroxine binding globulin, and growth hormone.
Hyperprolactinemia may be responsible for both reproductive and sexual disorders. Prolactin-secreting pituitary tumors, from microadenomy (less than 10mm) to macroadenomas, may lead to a decrease in libido, impotence, galaktoree, gynecomastia and cessation of spermatogenesis. Patients with macroadenomas generally in the first place of palpation complaint
violation of the fields of vision and headaches. In this situation it is necessary examinations, including CT or MRI scan of the pituitary, laboratory determination of hormones of the anterior pituitary, thyroid and adrenal glands. These patients indicated a decreased level of testosterone in the blood decrease or trends to the bottom of LH and FSH standards, reflecting the inadequate response of the hypophysis to reduce production of testosterone.
About 80% of male patients with hemochromatosis have testicular dysfunction. These patients may develop secondary hypogonadism in the background deposition of iron in the liver or may be primary, resulting in deposition of iron in the testes tissue. Iron deposition in hemochromatosis also detected in the pituitary gland, making the main source of pituitary disorders.
Regarding the role of exogenous hormones, the adrenal tumors, Sertoli cells, interstitial cells of the testes can produce estrogens. Cirrhosis of the liver accompanied by an increase of endogenous estrogens. First, estrogen suppresses the secretion of pituitary gonadotropins, and as a result of the development of secondary testicular failure. Androgens can also suppress the secretion of pituitary gonadotropins and promote the development of secondary testicular failure. Some athletes use anabolic steroids may lead to temporary infertility. Increased formation of endogenous androgens may occur as a result of androgen-producing adrenal tumors, testicular tumors, but the most common cause - congenital adrenal hyperplasia. In CAH increased formation of androgens adrenal cortex, leading to premature puberty and abnormally large size of the penis. Since the secretion of gonadotropins is suppressed, the testicles are not mature and have small sizes. In the absence of premature puberty diagnosis is extremely difficult, because the excess virilization difficult to distinguish from the normal sexually mature male.Need for a thorough laboratory examination. In diagnostically prescribed cases CAH infertility treatment is carried out using corticosteroids.Often physicians use corticosteroids in cases of idiopathic infertility. However, if during the survey cause of the violations do not have such therapy should not be used.
Sometimes, excessive use of glucocorticoids in the treatment of ulcerative colitis, asthma, rheumatoid arthritis leads to a decrease in spermatogenesis. Possible cause secondary testicular dysfunction - the suppression of LH secretion increased levels of plasma cortisol.Correction of an excess of glucocorticoids is accompanied by improvement of spermatogenesis.
Disruption of spermatogenesis may be due to malfunction of the thyroid gland. Hyper-and hypothyroidism can affect spermatogenesis.Hyperthyroidisim affects both the work of the pituitary, and in the testes, modifying the secretion of releasing hormones, and activating the conversion of androgens into estrogens in peripheral tissues.
Testicular causes of infertility
- Chromosomal abnormalities
- (Klinefelter syndrome, XX syndrome (syndrome of sexual reversion), XYY syndrome)
- Noonan's syndrome (a male version of Turner's syndrome)
- Myotonic dystrophy
- Bilateral anorchidism syndrome (absence of testes)
- Syndrome of the presence of only Sertoli cells (germ cell aplasia epithelium)
- Effect (drugs, radiation)
- Orchitis
- Injury
- Systemic diseases
(Renal failure, liver disease, sickle-cell anemia)
- Violations of the synthesis or the effect of androgens
- Cryptorchidism
- Varicocele
A number of anomalies in the structure of somatic chromosomes associated with male infertility. Examination of 1263 couples who applied to the problem of infertility, 6.2% of men were found chromosomal abnormalities. In a subgroup with decreased sperm count below 10 million / ml, the percentage of occurrence of chromosome abnormalities in males increased to 11% and in men with azoospermia the frequency of chromosome abnormalities was 21%. However, only in rare cases to confirm the relationship of infertility with specific chromosomal aberration, as DD translocation, ring chromosomes, reciprocal translocations and other aberrations. Nevertheless, to avoid anomalies of somatic and sex chromosomes in males with severe oligospermia or azoospermia should be conducted cytogenetic examination.
Klinefelter's syndrome - a genetic disorder associated with the presence of men more X-chromosome. It is dominated by two types of karyotype: 47XXY (classical form syndrome), or 46 XY/47XXY (mosaicism). The prevalence of the disease among men about 1:500. For these patients is characterized by dense, small testes, delayed sexual development, azoospermia, gynecomastia. Due to the fact that before puberty the characteristic signs of hypogonadism is not obvious, the diagnosis is usually established late. Reducing the size of the testicles usually occurs as a result of sclerosis of tubules. Typical sizes of eggs less than 2 cm in length and volume of less than 12 cm3.Characterized by increasing levels of LH and FSH. The level of testosterone varies from normal to reduced and decreases with age. The level of estradiol in the blood is usually elevated. Higher compared with the testosterone levels of estrogen lead to a feminization in the form of gynecomastia. Approximately 10% of these patients have chromosomal mosaicism. In these cases, the characteristic features of Klinefelter syndrome are less pronounced and men can be fertile in the event that there is a clone of a testicular cells containing normal set of chromosomes. Moderate dementia, restrictive lung pathology is encountered in these patients more frequently than in the population. Infertility in these patients is reversible and later the majority required replacement therapy with androgens in order to achieve optimal virilization and normal sexual function.
XX - violation or syndrome sex reversal
Klinefelter syndrome. Clinical symptoms are similar, except for below-average growth and hypospadias; cases of mental disability are less common. Patients have the karyotype 46HH. This paradox is explained by expression on cells of H-Y antigen and presumably the presence of the genome structures of Y-chromosome.
The frequency of XYY syndrome is approximately equal to the frequency of Klinefelter syndrome. Phenotypic manifestations of XYY syndrome are similar to Klinefelter syndrome, but more variable. Indicators of sperm in these men vary from normal to azoospermia. For patients, characterized by excessively high growth and acne, in a high percentage of cases observed antisocial behavior. The level of LH and testosterone levels in most patients is normal, and the level of FSH depends on the degree of damage to germ cells. Treatment of infertility does not exist.
Noonan's syndrome - male version
Turner syndrome (XO), and patients characterized by similar symptoms: small stature, wing folds on the neck, low-set ears, cubitus Valgus, visual disturbances and malformations of the cardiovascular system. Most men with Noonan syndrome occurs cryptorchidism, reduction of spermatogenesis and infertility. By reducing the function of testicular LH and FSH levels in the blood increased. Conducting cytogenetic survey reveals violations of sex chromosomes, such as mosaicism XO / XY. Treatments of infertility in these patients does not exist.
In patients with myotonic dystrophy observed violation of muscle relaxation after the initial reduction. The main clinical manifestations also include cataract, frontal baldness and testicular atrophy. The disease is inherited in an autosomal-dominant type and its manifestations are variable. .
Puberty usually occurs without singularities, and damage to the testicles develop later in adulthood. The function Leydig cells remains normal and gynecomastia is not observed.
Bilateral anorchidism or absence of the testes syndrome is very rare, approximately 1:20000 men. In these patients the testicles at birth are not defined and later, due to lack of synthesis of androgens in the testes, develops sexual immaturity. Karyotype of the patient are normal; LH and FSH levels increased and testosterone levels are very low. During the intrauterine period of development of the testes may be lost as a functioning organ trauma, torsion, vascular injury or infection. Nevertheless, in order to occur differentiation of the reproductive system of male type, functioning tissue testes should be present at least during the first trimester prenatal period. In response to hCG stimulation of testosterone does not increase. For patients characterized thin physique. Gynecomastia is not typical. In the course of treatment is only possible correction of deficiency of testosterone. Treatments of infertility in these patients does not exist.
Syndrome of the presence of only Sertoli cells or germ cell aplasia of the epithelium, may be due to different causes: congenital absence of germ cell epithelium, genetic defects, resistance to androgens. When testicular biopsy revealed a complete absence of germinal epithelium, and clinical examination azoospermia in conjunction with normal virilization, testicular consistency was normal, but their size somewhat reduced, gynecomastia does not. Testosterone and LH in normal, but FSH levels are usually elevated. Sometimes patients with other diseases testes (mumps, cryptorchidism, damage from radiation and toxic exposure), seminiferous tubules may also contain only Sertoli cells, but these patients will be reduced testes size, and histological examination of the material is uneven. As the characteristic features of these patients more frequently observed sclerosis and hyalinosis. Infertility treatment is not effective.
drugs and radiation may have a damaging effect on the germ cell epithelium, because germ cell epithelium - a rapidly dividing tissue, and the process of cell division is most sensitive to the damaging effects. Chemotherapy of cancer has a dose-dependent effect on the germ cell epithelium. In the period preceding the sexual maturation of germinal epithelium of the testes is more resistant to the toxic effects of drugs than in adulthood. Alkylating drugs used in chemotherapy, such as hiromantin, cyclophosphamide toxicity have damaging effect on the testes. A number of patients before chemotherapy may conduct cryopreservation of sperm. Cyproterone, ketoconazole, spironolactone, alcohol contribute to disruption of synthesis of testosterone. Cimetidine - testosterone antagonist, blocks the peripheral action of testosterone in target-tissues. Frequent side effects - gynaecomastia and reduced sperm count. Narcotic drugs such as marijuana, heroine, methadone leads to a lower level of testosterone in plasma, without a concomitant increase LH. This indicates that both the violation of central origin, and violations at the level of the testes. Discovered weakening testicular function under the influence of some pesticides, for example, dibromohlorpropana. Particularly sensitive to radiation, germ cell epithelium, while Leydig cells are relatively stable. Irradiation with a dose of less than 600 rad leads to a reversible cell damage eggs. At higher levels of exposure are more likely occurrence of persistent violations.Recovery of spermatogenesis may take 2-3 years even in men who have undergone low doses of radiation. Elevated levels of FSH reflects a weakening of spermatogenesis. When restoring testicular function of FSH levels returned to normal.
In 15-20% of adult men mumps can lead to the development of orchitis, usually unilateral. Bilateral orchitis occurs in about 10% of cases.Within 1 to 6 months, or within a few years after the disease may develop testicular atrophy. Normal rates of sperm recovered less than 1 / 3 of men.
Such systemic diseases such as renal failure, accompanied by a male decreased libido, impotence, a violation of spermatogenesis, gynecomastia. LH and FSH levels increased, and testosterone levels decreased. The cause of hypogonadism in uremia multifactorial. Every fourth patient with uremia found elevated prolactin levels. Additional contributions can make an excess of estrogen. Antihypertensive drugs, uremic neuropathy may also play a role in the development of impotence and hypogonadism. After successful kidney transplantation for uremic hypogonadism improves. In a large percentage of men with liver cirrhosis observed testicular atrophy, impotence, and gynecomastia.Testosterone reduced, while the level of estradiol increased due to the simultaneous decrease in the synthesis of androgens in the liver and increase the peripheral conversion to estrogens. At relatively low levels of serum testosterone observed a moderate increase in LH and FSH.Also, to reduce blood levels of testosterone causes alcohol, due to suppression of testosterone synthesis in the testes. For the majority of men with sickle cell anemia is characterized by symptoms of hypogonadism. Although LH and FSH levels may be different levels of testosterone decreased. Hypogonadism with sickle-cell anemia may develop secondary to the testicular and hypothalamic-pituitary disorders.
Rare inherited disorders of enzymes involved in the synthesis of testosterone, accompanied inadequate virilization, to be seen at birth in the form of hermaphroditism. Some forms of androgen resistance leads to a lack of virilization, infertility and the development of male sexual characteristics of female type. Diagnosis is based on the detection of abnormal androgen receptors in skin fibroblast culture genitals.Interestingly, the level of testosterone and LH increased. Diagnosis of these disorders is expensive, but effective treatments for infertility does not exist.
Cryptorchidism occurs in 0.8% of adult men. Morphological changes in the retained testis begin to develop after 2 years of age. Despite prophylactic holding, patients suffering from unilateral cryptorchidism have reduced fertility potential. Especially strongly disturbed sperm quality in men with bilateral undescended testes. Although basal levels of LH, FSH and testosterone may be normal, LH and FSH response to GnRH stimulation elevated, which may reflect a violation of testicular function.
Varicocele scrotum - one of the most frequent findings in men who have addressed the problem of infertility. The cause of varicocele - violation outflow of blood due to deficiency or absence of valves seminal veins. Such a defect in the valve apparatus in combination with the long vertical course of the internal spermatic vein on the left leads to more frequent formation shift to the left varicocele (90% of). Internal seminal Vienna has a right oblique stroke, and therefore the right varicocele is usually not determined. The appearance of a unilateral, located right varicocele may be a consequence of venous thrombosis, tumors or in situ inversus. Studies using modern diagnostic techniques show the occurrence of bilateral varicocele in more than 40% of cases. Among men the prevalence of varicocele is approximately 21%, and a group of men suffering from infertility, this figure increases to 40%. Approximately 50% of men with varicocele revealed deterioration of sperm quality, although it is also many men fertility of sperm stored. The following assumptions mechanisms violation of spermatogenesis in men with varicocele:
- Increasing the temperature in the testicles due to venous stasis
- Retrograde flow of toxic metabolites from the adrenal glands and kidneys
- Stagnation of blood with the development of hypoxia germ cell epithelium, and
- Changes in the functioning of the hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular axis
These recent experimental results confirm investigates the connections between increased blood flow, raising the temperature in the testes and disruption of spermatogenesis.
Unfortunately, 25-40% of men with infertility are diagnosed with idiopathic male infertility when the cause cannot be established. With the advancement of our knowledge about the physiology of the male reproductive system of a group of patients with unexplained infertility will gradually decrease.
post testicular infertility
Disorders of sperm transport
Congenital
Acquired violation
Functional disturbances
Violations of mobility or function of sperm
Congenital malformations of the sperm tail
Violation of sperm maturation
Immunological disorders
Infections
Sexual dysfunction
Violations of the transport of sperm
Congenital anomalies of sperm transport are rare and are caused by the absence or atresia tubular sections of the male reproductive tract. In men with fibrosis of the bladder increased frequency of congenital hypoplasia or absence of the main body of the epididymis, spermatic cord and seminal vesicles. The absence of seminal vesicles is always accompanied by azoospermia, a violation of coagulation of semen during ejaculation, and lack of fructose in semen. Young's syndrome associated with pulmonary pathology, ultrastructure of the cilia is normal, but the outflow of sperm from the epididymis is difficult due to thickening of sperm that leads to azoospermia.
Acquired violations transport of sperm, usually associated with bacterial infections that lead to the development of acute or chronic inflammation in the epididymis, with subsequent formation of scar tissue and obstruction. In addition to vasectomy, random ligation of spermatic cord is possible with surgical treatment of inguinal hernias, and even during varicostomy.
Functional obstruction of sperm transport is the result of innervation in the sympathetic nerve injury during surgical removal of retroperitoneal lymph nodes are located, or in operations on the pelvic organs. Innervation may cause the insufficient reduction of spermatic cord with subsequent failure of issue, as well as violation of reducing the bladder neck during ejaculation and, as a consequence - retrograde ejaculation. Damage to the spinal cord can lead to para-and tetraplegia, followed by erectile dysfunction and a violation of emission and ejaculation. Disrupt the sympathetic nervous system may be many medications such as tranquilizers, antidepressants, antihypertensive drugs.
Violation of mobility and function of sperm
Violation of mobility and function of sperm develops secondarily as a result of congenital defects of the sperm tail, disrupting the maturation of sperm, immunological disorders.
Ciliary dyskinesia syndrome - a group of diseases characterized by immobility, a deterioration of sperm motility, such as Kartagener syndrome. In these diseases results in normal testicular biopsy, sperm count in the fracture normal, but sperm motility or significantly reduced, or sperm immobile. Ultrastructural defects, leading to disability as cilia and sperm, can be seen only by electron microscopy. The defects underlying the ciliary dyskinesia syndrome, include the lack of dineinovyh pens, short or absent radial connection without a central cover and lack of central microtubules. Violation of sperm motility Mauger also be due to the lack of protein in sperm tail.
The normal number but reduced motility may occur after vasectomy due to dysfunction epididymis. Chronic increase internal pressure that occurs after vasectomy, can have a negative effect on the epididymis - sperm cannot pass the normal stages of maturation and acquire mobility. Violation gamato-testicular barrier as a result of infection, trauma or surgery is accompanied by sensitization of the organism with antigens of spermatozoa. Antisperm antibodies play a role in the development of infertility in 3-7% of infertile men. Immune disorders are usually not the absolute cause of infertility in the patient, but can reduce the fertility of sperm.
Infections. High concentrations of gram-negative bacteria such as E. coli, in the sperm can reduce sperm motility. Urogenital infections such as chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis, rarely cause infertility. Studies in both animals and humans have not produced convincing evidence to support the need for bacteriological culture or empirical antimicrobial therapy in asymptomatic infertile men.
Sexual dysfunction was observed in 20% of infertile men. Reduced sexual desire, erectile dysfunction, premature ejaculation – potential cause reproductive failure. Reduced libido and erectile dysfunction can be due to low testosterone levels associated with organic pathology.
Diagnostic tests & Sperm Counts
Despite the fact that semen analysis is not a test for fertility, careful study to evaluate the functional state of hormonal regulation, spermatogenesis and the patency of the reproductive tract. The only true indicator of fertility - is pregnancy and this phenomenon is associated with the state of the couple as a whole. It must be borne in mind that the boundaries of normal values of sperm is difficult to determine in healthy men in their reproductive period. Clinical studies of patients with infertility have allowed to establish "normal ranges", below which the chances of pregnancy reduced. These boundaries are not absolute, because some fertile male semen parameters may be below the limit of normal. Conversely, men who addressed the problem of infertility in the standard survey methods may have had normal sperm, because the standard survey does not assess the functional ability of sperm. In the conduct of sperm is strongly recommended to use the "Laboratory guide to the analysis of human sperm and the interaction between sperm from the cervix, the World Health Organization (WHO). Most experts are exploring at least three semen samples, indicators of which differ from each other within 20%, before the conclusion about the state of the sperm. To analyze the best use of a sample of sperm obtained by masturbation after 2-3 days abstinence from sexual activity. The study sample should be held within 1-2 hours after receipt. Also for the analysis is possible, but less desirable to use samples of semen obtained by coitus interruptus or silicone condom that does not contain spermicides. Therefore, it is best if the samples of sperm are obtained directly from the venue of the study. In addition to the errors in the conduct of research in the laboratory, in different samples of semen obtained from the same man, indicators such as density, motility and morphology of spermatozoa may vary. In many respects, such a variation of indicators affects the long period of abstinence. With each additional day of abstinence (up to 1 week) increases the amount of seed to 0.4 ml, sperm concentration of 10-15 million, and total sperm count 50-90 million sperm motility and morphology does not change over the next 5-7 days abstinence but longer term a decline of sperm motility. Interpreting the results of semen analysis should take into account the differences between the different samples.
https://bayanlarsitesi.com/
ReplyDeleteGöktürk
Yenidoğan
Şemsipaşa
Çağlayan
TOQGHJ
Muğla
ReplyDeleteSamsun
Eskişehir
Sakarya
Kars
BWLTUK
Mardin
ReplyDeleteistanbul
Çanakkale
Antep
Elazığ
F6LGR
Konya
ReplyDeleteKayseri
Malatya
Elazığ
Tokat
ND0İ2
bitlis
ReplyDeleteurfa
mardin
tokat
çorum
JQWİ0K
yozgat
ReplyDeletesivas
bayburt
van
uşak
REHU
görüntülü show
ReplyDeleteücretlishow
53UK2Q
Çorlu Lojistik
ReplyDeleteManisa Lojistik
Eskişehir Lojistik
Afyon Lojistik
Konya Lojistik
W4YGL
60E42
ReplyDeleteArdahan Şehir İçi Nakliyat
Kalıcı Makyaj
Denizli Şehir İçi Nakliyat
Trabzon Şehir İçi Nakliyat
Ankara Fayans Ustası
Ankara Boya Ustası
Zonguldak Evden Eve Nakliyat
Batıkent Fayans Ustası
Kırşehir Parça Eşya Taşıma
44687
ReplyDeleteIğdır Evden Eve Nakliyat
Bitlis Şehir İçi Nakliyat
Gümüşhane Şehir İçi Nakliyat
Bartın Şehir İçi Nakliyat
Bartın Parça Eşya Taşıma
Karabük Lojistik
Çerkezköy Halı Yıkama
Gümüşhane Evden Eve Nakliyat
Sincan Parke Ustası
D2591
ReplyDeleteKilis Lojistik
Çerkezköy Çatı Ustası
Tekirdağ Parke Ustası
Çankırı Parça Eşya Taşıma
Ankara Asansör Tamiri
Bitlis Parça Eşya Taşıma
Malatya Evden Eve Nakliyat
Tokat Parça Eşya Taşıma
Artvin Lojistik
BAD96
ReplyDeleteBinance Güvenilir mi
Kırklareli Evden Eve Nakliyat
fat burner for sale
Çankırı Evden Eve Nakliyat
parabolan for sale
Rize Evden Eve Nakliyat
Antep Evden Eve Nakliyat
Tekirdağ Evden Eve Nakliyat
Hakkari Evden Eve Nakliyat
10E54
ReplyDeleteİzmir Parça Eşya Taşıma
Bilecik Şehir İçi Nakliyat
Ünye Petek Temizleme
Gölbaşı Fayans Ustası
Mardin Parça Eşya Taşıma
Düzce Parça Eşya Taşıma
Erzurum Parça Eşya Taşıma
Etlik Fayans Ustası
Samsun Parça Eşya Taşıma
53F15
ReplyDeleteafyon telefonda sohbet
karaman canlı sohbet siteleri
aydın görüntülü sohbet siteleri
bitlis mobil sohbet chat
zonguldak rastgele görüntülü sohbet uygulaması
mardin canlı sohbet bedava
sesli sohbet siteleri
bilecik sesli sohbet
muhabbet sohbet
CB0E1
ReplyDeleteFlare Coin Hangi Borsada
Parasız Görüntülü Sohbet
Bitcoin Nasıl Kazanılır
Yeni Çıkacak Coin Nasıl Alınır
Pepecoin Coin Hangi Borsada
Arbitrum Coin Hangi Borsada
Chat Gpt Coin Hangi Borsada
Bonk Coin Hangi Borsada
Twitter Retweet Hilesi
E3DA4
ReplyDeleteLinkedin Takipçi Hilesi
Soundcloud Beğeni Satın Al
Threads İzlenme Satın Al
Binance Referans Kodu
Bitcoin Giriş Nasıl Yapılır
Bonk Coin Hangi Borsada
Binance Hesap Açma
Bitcoin Çıkarma Siteleri
Likee App Takipçi Satın Al
42110
ReplyDeleteMexc Borsası Kimin
Big Wolf Coin Hangi Borsada
Bitcoin Nasıl Çıkarılır
Soundcloud Takipçi Satın Al
Dlive Takipçi Satın Al
Bitcoin Madenciliği Nedir
Threads Yeniden Paylaş Satın Al
Bitcoin Giriş Nasıl Yapılır
Görüntülü Sohbet
65CF8
ReplyDeleteBitcoin Para Kazanma
Kripto Para Çıkarma
Coin Nedir
Parasız Görüntülü Sohbet
Facebook Beğeni Hilesi
Kripto Para Madenciliği Siteleri
Binance Hangi Ülkenin
Aion Coin Hangi Borsada
Ön Satış Coin Nasıl Alınır
A9C31
ReplyDeletepoocoin
raydium
galagames
arculus
trezor suite
dcent
shiba
sushi
poocoin
66BC7546DE
ReplyDeletetelegram cam show
716FBCDCB0
ReplyDeletetürk takipçi